Writing drivers
What is an EVL driver?
An EVL-enabled character device driver is a regular driver which also
implements a set of out-of-band I/O operations advertised by its file
operation descriptor (struct file_operations). These out-of-band I/O
requests are only available to EVL threads, since only such threads may run on the
out-of-band execution stage. Applications
running in user-space can start these I/O operations by issuing
specific system calls to the EVL
core.
Excerpt from include/linux/fs.h, as modified by Dovetail
struct file_operations {
...
ssize_t (*oob_read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t);
ssize_t (*oob_write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t);
long (*oob_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
long (*compat_oob_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
__poll_t (*oob_poll) (struct file *, struct oob_poll_wait *);
...
} __randomize_layout;An EVL-enabled network device driver is a regular network device driver at its core, which in addition implements some support to handle network traffic directly from the out-of-band stage, as explained in this document. In the particular case of the socket interface, Dovetail also connects the in-band networking core with the companion core through a simple internal interface so that the latter can provide out-of-band extensions.
Dovetail is in charge of routing the system calls received from applications to the proper recipient, either the EVL core or the in-band kernel. As mentioned earlier when describing the everything-is-a-file mantra, only I/O transfer and control requests have to run from the out-of-band context (i.e. EVL’s real-time mode), creating and dismantling the underlying file from the regular in-band context is just fine. Therefore, the execution flow upon I/O system calls looks like this:
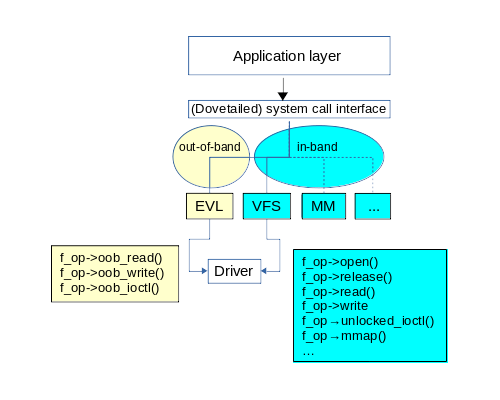
Which translates as follows:
-
When an application issues the open(2) system call of an EVL-enabled charcacter device driver, the latter attaches an out-of-band extension to the underlying file.
-
When any of the close(2), mmap(2), ioctl(2), read(2), write(2) system calls are invoked for a file descriptor which refers to an out-of-band extended file, the request normally goes through the virtual filesystem switch (VFS) as usual, ending up in the regular handlers pointed at by the file operation structure. The same goes for all other common file operations for character device drivers.
-
When an applications issues the oob_read(), oob_write() or oob_ioctl() system calls via the EVL library, Dovetail routes the call to the EVL core (instead of the VFS), which in turn fires the corresponding handlers defined by the driver’s
struct file_operationsdescriptor: i.e..oob_read(),.oob_write(), and.oob_ioctl(). Those handlers should use the EVL kernel API, or the main kernel services which are known to be usable from the out-of-band-context, exclusively. Failing to abide by this golden rule may lead to funky outcomes ranging from plain kernel crashes (lucky) to rampant memory corruption (unlucky).
Tip
Now, you may wonder: “what if an out-of-band operation is ongoing in
the driver on a particular file, while I’m closing the last
VFS-maintained reference to that file?” Well, with a properly written
EVL driver, the
close(2) call
should block until the out-of-band operation finishes, at which point
the .release() handler may proceed with dismantling the file. A
simple rule for writing EVL
drivers ensures this.
